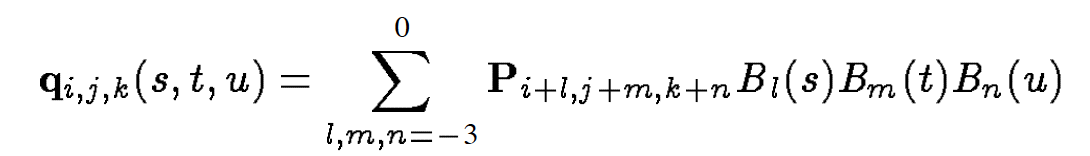Mapping from 2D to 3D: There is ambiguity when mapping a vertex's screen position to its position in model space. When single point is selected, the mapping is done by transforming the vertex position(3D) and the displacement(2D mouse movement in screen space) into clipping space and combine these two, assuming no depth displacement. And the result is then transformed back to model space. This method ensures that the displacement in screen space of the control point is exactly the displacement of the mouse. However, when multiple control points are selected, the z-value of the control point that is closest to the view direction (in clipping space) is used for movement of all control points. In reality, this is more intuitive.
Stroke segment for bending: In Draper and Egbert's paper, the stroke is divided to segments of equal distance. However, for Kivy(i.e. graphics kit used for the project), the mouse_move event is not recorded frequently, hence it is hard to obtain equal-distanced segements. Therefore, the recorded mouse position is uniformly sampled. The result of this solution will therefore be affected by the speed of the mouse stroke. Which might be desired in some cases.
.obj file processing: .obj files does not provide a 1-1 mapping from vertex to normal, which is less ideal for the purpose of performing FFD. The approach I took is to first build a 1-1 map of vertex and normal and use this map to perform the FFD. Only indices of vertices are stored for every faces, and the normals are then retracted from the map.
Normal Calculation: There is no direct methods of calculating normals for a tri-variate tensor product at a single point. The approach I took is that for each vertex, first find two vector spanninf the tangent plane at that point. Then two points are chosen epsilon-distance along each vector from the vertex. This face (vertex+two extra points) therefore captures the local curvature of the surface. The three points are deformed together. The new normal of the vector is assigned to be the normal of this deformed face. In practice, this gives faily smooth shading result.